What are Haplogroups, and how do they work?
 Arberian 10/05/2024
Arberian 10/05/2024 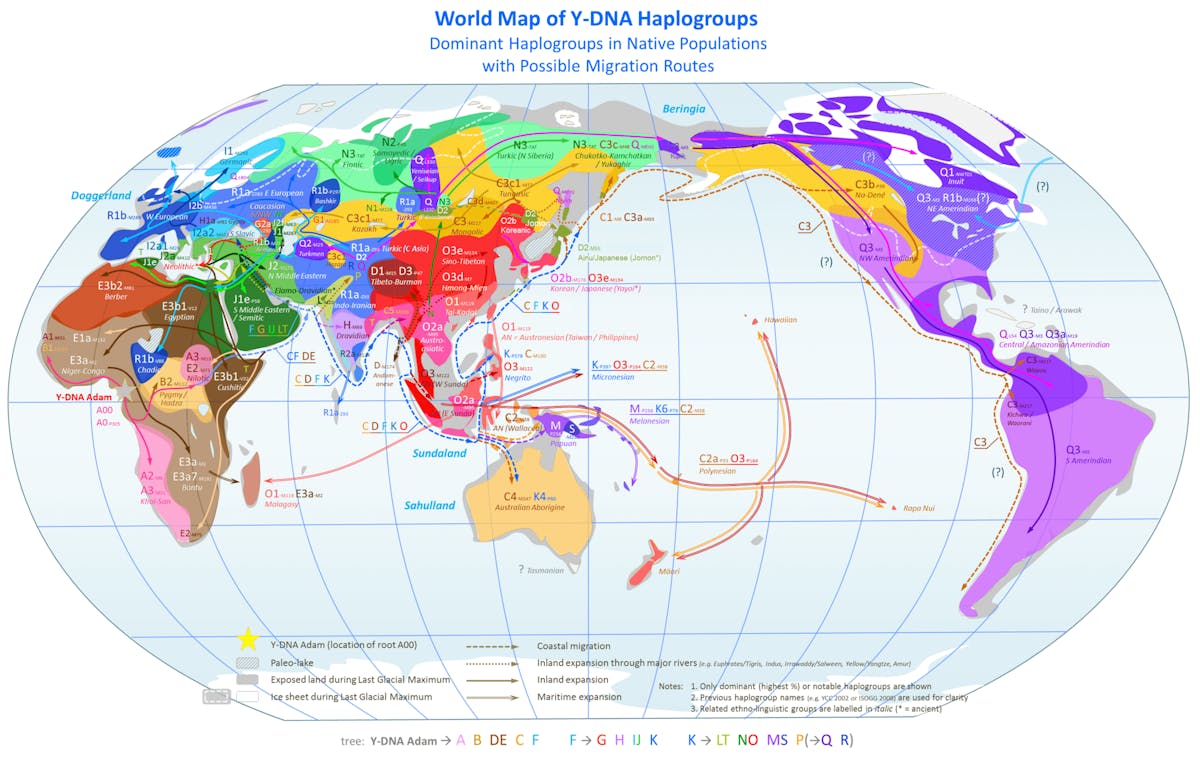
What is a Haplogroup? Haplogroups are groups of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a specific genetic mutation. They can be used to trace lineage and migrations over thousands of years. Y-DNA haplogroups trace paternal lineage, while mtDNA haplogroups trace maternal lineage.
A male has both X & Y-DNA, X inherited from the Mother and Y from the Father, while a female only has X, since the Y-DNA Haplogroup is only inherited from the Father
Here's some examples on how Autosomal DNA and Y & X Chromosomes gets inherited.


What is Y-DNA? Y-DNA (Y-Chromosome DNA) refers to the DNA located on the Y chromosome, which is passed down from father to son. This type of DNA changes very little over generations, making it useful for tracing paternal lineage far back in time. It helps us understand your direct paternal ancestors and their migrations over thousands of years.
How do you know if an individual descends from a Group of other Populations instead of his? Haplogroups indicate the populations to which a group is most genetically similar, while haplogroup subclades reveal even closer genetic connections. For example, if a Serb belongs to a Paleo-Balkanic lineage (For example J-L283), if in the same lineage Albanians are present, it suggests that the Serb has Albanian ancestry. Conversely, if an Albanian shares a Slavic haplogroup (R1a-M458+, I2-Y3120+) with Serbs or other South Slavs, it implies that the Albanian has South Slavic paternal ancestry.
Here's two examples from Y-Full.


What is TMRCA (Time to Most Recent Common Ancestor)? TMRCA is a term used to describe the estimated time when two individuals share a common ancestor. This concept is particularly useful in genetic genealogy to understand how closely related you are to another person or group. TMRCA can provide insights into how recently two family lines have diverged.

About Arberian
An Albanian, interested in history and genetics.